It's no secret that managing organic waste is a massive headache. Landfills are overflowing, wastewater treatment plants are under pressure, and dairy farms struggle with methane emissions from manure, but Biogas Capture can truly help. 1 Without biogas capture this isn't just bad for business; it's a climate concern too. Methane, the pesky gas released by all that decomposing organic matter, is over 80 times more powerful than carbon dioxide at trapping heat in the atmosphere.
Here's some good news: Biogas Capture (US terminology for anaerobic digestion) is flipping this problem on its head. By turning waste into renewable energy, the U.S. has seen record growth in this sector's 13% higher output capacity and a 40% jump in investment just last year! (2024) 3 In 2025, even bigger leaps are expected as new facilities come online and innovative tech gets to work. 2
This blog will show you how biogas capture is reshaping waste management across landfills, dairy farms, and wastewater treatment plants while opening doors to greener energy solutions.
Ready to see what's ahead? Read on it only gets better from here!
Key Takeaways
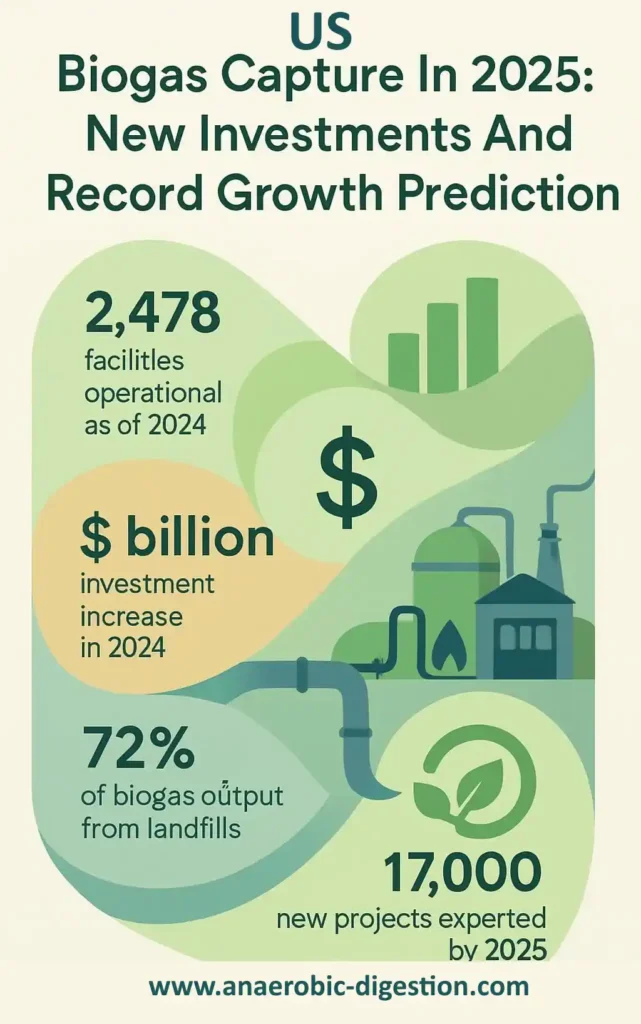
- The U.S. biogas sector is growing rapidly, with 2,478 facilities in operation as of 2024, accounting for only 10% of potential capacity (ABC). Over 17,000 new projects are expected by 2025.
- US investments surged by $3 billion in 2024, a 40% increase over the previous year, driven by rising energy demands and methane reduction goals.
- U.S. landfills dominate biogas output at 72%, but agricultural systems grew four times faster than landfill gas projects in recent years (ABC). Dairy farms contribute to over a quarter of existing facilities.
- Renewable natural gas (RNG) production soared, with capacity climbing by 170% since 2020. Nearly all new biogas plants built in recent years targeted RNG production due to higher financial returns.
- Federal policies like the Renewable Fuel Standard and programs such as the Inflation Reduction Act continue boosting investments and growth across sectors like agriculture and wastewater treatment plants.
What is biogas capture? In the Dairy Farm, Wastewater Treatment and Landfill Gas Sectors
Biogas capture collects methane from organic waste like manure, sewage sludge, and decomposing landfill materials. This process uses anaerobic digesters to break down these wastes in oxygen-free environments.
Methane produced during this breakdown is harvested as renewable natural gas or biogas for energy production.
Dairy farm biogas facilities produce 25% of U.S. renewable methane. 1 These systems turn animal waste into energy while reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Landfill sites host 23% of facilities but contribute an overwhelming 72% of the nation's biogas capacity by capturing methane from the organic matter in decaying garbage.
Wastewater treatment plants account for nearly half, using sewage sludge to generate power efficiently. 1
“Every ton of organic waste turned into energy reduces harmful methane emissions significantly.”
The US Biogas Capture Industry in 2025 in the Dairy Farm, Wastewater Treatment and Landfill Gas Sectors

The U.S. biogas sector is charging ahead, fueled by rising energy demands and methane reduction targets. New facilities for capturing gas from manure, sewage, and landfills are reshaping waste management and renewable energy efforts.
Biogas Capture growth reported by the American Biogas Council
The American Biogas Council (ABC) forecasts an eight-fold rise in biogas energy production by 2025. 2 They expect 17,000 new biogas projects to come online across the nation. This projection signals a major uptick in renewable energy generation from sources like dairy farms, landfills, and wastewater treatment plants.
In just 2024 alone, operational biogas facilities grew by 17%. Capital investment also surged that year with a staggering increase of 40%, showing how rapidly this sector is scaling up.
States like Iowa, Minnesota, and North Carolina are identified as hotspots for growth due to abundant organic waste supplies. 2 Across North America, only about 10% of potential landfill gas capture systems have been developed so far.
This leaves massive opportunities untouched for reducing methane emissions while creating renewable fuels like biomethane or compressed natural gas. These trends point toward record-setting advancements in converting waste into power and fuel solutions over the next two years.
Capitalizing on this momentum ties directly into policy changes discussed during ABCâs briefings on industry progress and challenges related to organic material recycling for energy recovery systems.
ABC's media briefing on biogas capture industry status, progress, potential, and policy implications
ABC revealed promising trends in biogas capture during their recent briefing. 3 The U.S. currently operates 2,478 biogas facilities, but this reflects only 10% of its potential capacity. 3 Experts emphasized expanding these systems to handle the nationâs significant organic waste volumes: over 1.4 billion tons of manure and millions more from food scraps and biosolids annually.

Organic Waste Generation in the U. S. available for Biogas Capture from Dairy Farm Waste, Wastewater Treatment, and Landfill Gas Sectors
Farm manure, food scraps, and yard waste pile up across the U.S., creating mountains of unused energy. These materials could power communities instead of sitting idle or being flared into the sky.
Breakdown of annual organic waste generation
The U.S. generates an enormous amount of organic waste that can be captured for biogas production. Here's a snapshot of the annual waste breakdown across key sectors:
| Source | Waste Type | Annual Generation (Tons) | Potential for Biogas Capture |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dairy Farms | Manure | 1.4 billion | High |
| Food Supply Chain | Inedible Food Waste | 33 million | Medium |
| Wastewater Treatment Plants | Biosolids | 1 million | High |
| Landfills | Flaring Landfill Gas | Significant Portion of Total Organic Waste | Largest Contributor |
This provides a clear view of waste sources and their respective opportunities. Next, let's explore how captured biogas from these materials fuels energy production. 4
Landfills flaring capturable gas
Landfills in the United States flare massive amounts of methane-rich gas instead of capturing it. Out of 470 active landfills, many burn off this gas as a safety measure or waste disposal method. 5 This process releases unutilized energy that could otherwise generate electricity or fuel for industries and homes.
Capturing landfill gas offers more than just an energy solution. Methane emissions contribute significantly to climate change, but biogas systems can cut down these greenhouse gases effectively.
With over 20,000 potential projects identified by the American Biogas Council, investing in biogas plants is both practical and necessary. Organic material like manure and food scraps dumped into landfills adds to the problem if not redirected toward renewable energy production.

Captured Biogas Production from Organic Materials, in the Dairy Farm, Wastewater Treatment and Landfill Gas Sectors
Farm manure, food scraps, and sewage sludge fuel biogas systems through anaerobic digestion. These systems recycle waste into energy that powers homes and industries while slashing greenhouse gases.
Processes for producing biogas from organic materials
Anaerobic digestion breaks down organic waste like manure, food scraps, and grease in airtight tanks. Microbes digest the material without oxygen, creating biogas rich in methane and carbon dioxide.
This process produces energy and leaves behind digestate that can be used as animal bedding or fertilisers. 6
Nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are recovered after digestion. These nutrients improve soil quality while decreasing the dependence on synthetic fertilisers. Landfills with gas collection systems capture methane emissions for energy production, too.
Recycling organic materials for energy production
Dairy farms, landfills, and wastewater treatment plants serve as goldmines for organic materials. Livestock manure from farms creates biogas through anaerobic decomposition. This process traps methane (CH4) that would otherwise pollute the air.
Landfills also release methane when organic waste decays under layers of waste. Instead of flaring this capturable gas, facilities transform it into renewable natural gas (RNG). 7
Wastewater treatment plants take a similar path by recycling sewage sludge. They convert this waste into energy using combined heat and power (CHP) systems. These systems generate both electricity and heat from captured biogas at the site itself.
With over 1,418 facilities producing electricity in 2024 alone, advanced biofuels have become an ideal low-carbon fuel standard option for clean energy production in America today!

Growth and Investment in the Biogas Capture Industry
Investors are pouring funds into biogas capture facilities as demand for renewable energy surges. New projects spotlight agriculture and wastewater treatment as game-changers for clean energy production.
Number of biogas capture facilities in the U.S.
Biogas capture facilities in the U.S. have seen major growth over recent years. Hereâs how the numbers stack up.
| Year | Total Biogas Facilities | Growth (%) | Facility Types & Share |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 2,135 | 17% |
|
| 2025 (Projected) | ~2,500 | 17%+ |
|
Wastewater treatment plants dominate, hosting nearly half of these facilities. 8 The agricultural sector makes up around a quarter. Compared to the prior year, agricultural digester installations climbed 24%. 8 These added 615 operations nationwide by 2024.
The country now runs almost 2,500 facilities as of 2025. This expansion continues to highlight the tremendous focus on harnessing renewable energy sources while addressing waste challenges. 9
Potential for additional systems based on available organic material (Dairy Farm and Wastewater Treatment Sectors)
The U.S. holds the potential for 24,000 new biogas systems. Farms could house up to 17,000 of these projects, while wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) account for another 4,000. 4 The dairy sector alone drives 85.9% of farm-based biogas production using manure as a feedstock. 4 Many WWTP facilities also handle food waste alongside biosolids.
Currently, about 200 agricultural and WWTP systems recycle organic material like manure and wastewater into energy sources such as renewable natural gas (RNG). With additional setups targeting excess nutrients and reducing fossil fuel reliance, there's room to expand this industry further in rural areas and urban centers alike.
Growth in captured output is strongly tied to policies discussed under “2025 Growth and Investment”.
2025 Growth and Investment in the Dairy Farm and Wastewater Treatment Sectors for Biogas Capture
Businesses are pouring more money into biogas systems on dairy farms and wastewater plants. These investments aim to boost energy recovery while slashing greenhouse gas emissions.
Increase in captured biogas output capacity and investment
Investments in U.S. biogas systems surged by $3 billion in 2024, marking a 40% increase from the prior year. 10 This jump saw the number of operational biogas facilities rise to 2,478, with 125 new sites coming online.
Landfill gas projects still dominate the sector, delivering about 72% of all outputs and largely generating electricity for local grids. Renewable natural gas (RNG) capacity experienced explosive growth, too, climbing an astounding 170% between 2020 and last year.
Dairy farms and wastewater treatment plants now show massive potential for additional systems due to untapped organic waste resources. Current trends reveal increasing attention shifting toward these agricultural sectors as opposed to landfills alone.
With consistent financial backing and growing public interest in low-carbon fuels like RNG, more capture facilities are set on reducing reliance on fossil fuels while supporting energy transitions into greener alternatives.
Moving further into RNG production statistics unveils even more about this dynamic industry's trajectory ahead.

Shift in agricultural biogas projects compared to landfill projects
Farm-based biogas systems saw a major surge in 2024, growing four times faster than landfill gas projects. 10 Agricultural investments outpaced those in landfills for the first time, proving a shift in priorities.
Over 615 new agricultural biogas projects were launched that year alone, while postconsumer food waste processing by anaerobic digestion sat at just 14%. 10 This highlights untapped potential within the agriculture sector.
Landfill flaring remains common but lags behind agricultural efforts. The low-carbon fuel standard and other green energy policies have bolstered farm-centred developments. These projects now focus on recycling organic wastes like dairy manure into renewable natural gas (RNG).
This progress reflects growing opportunities to decarbonize rural energy systems beyond traditional methane recovery facilities at landfills.
RNG Production and Facility Distribution
RNG production facilities that use captured biogas in its purified methane state are springing up faster than ever, transforming organic waste into a clean energy capture powerhouse.
These plants fuel buses, power grids, and even some industrial engines with renewable natural gas.
Increase in RNG production and facility statistics
RNG production in the U.S. has been on a sharp upward trajectory. Waste management professionals have witnessed a surge in facilities and capacity in recent years. Below is a snapshot outlining this growth in simple terms.
| Year | Number of US RNG Facilities | Growth in US RNG Capacity |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 338 | Baseline |
| 2023 | 781 | +110% |
| June 2025 | 914 | +170% (since 2020) |
This growth isn't just numbers on paper. California and Texas have set the gold standard with robust expansions in infrastructure. These states lead in pushing RNG capacity higher. 11
The numbers tell the story. In the US, between 2020 and 2024, RNG capacity skyrocketed by 170%. Facilities jumped from 338 in 2020 to 914 by mid-2025. Each facility brings the industry closer to meeting energy goals.
It's not just wastewater and food waste fueling this shift. Nearly 1 million dry tons of wastewater sludge and 33 million dry tons of inedible food waste are waiting to power even more systems. These materials are the backbone for RNG production, offering untapped opportunities for states and municipalities.
California's focus on clean energy policies keeps it ahead in RNG output. Texas leverages its scale and resources to expand production. Both states demonstrate what's possible with consistent investments and forward-thinking initiatives.
This sector's rapid growth has put it on the map. More facilities mean more captured energy, reduced emissions, and better waste management practices. Waste management professionals, the runway for progress is long and wide.
Focus on RNG production goals
The push for RNG production saw groundbreaking strides in 2025. Nearly 95% of new biogas projects aimed to produce renewable natural gas. 12 Facilities across dairy farms, landfills, and wastewater plants shifted priorities to meet rising demand.
RNG purified from US biogas accounted for about 40% of the total available biogas output in that year alone. 12
States like California, Illinois, and South Dakota led investments with over $850 million dedicated to landfill-to-RNG conversions by the end of 2024. These projects offered less costly setups and consistent gas yields.
The steady supply also helped generate valuable regulatory credits under federal programs such as the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS). Waste management professionals backed this transition as an essential strategy for cleaner energy goals nationwide, keeping bioenergy competitive against fossil fuels like coal or oil.
Policies and Support for the Biogas Capture Industry
Lawmakers push for cleaner energy through incentives like the Inflation Reduction Act. Federal programs fuel biogas projects, turning waste into power sources nationwide.
Bipartisan support and effective policies
Michigan recently passed waste-to-energy legislation, showing strong bipartisan backing in renewable energy. 13 The American Biogas Council (ABC) continues to push for reforms, like expanded tax credits and streamlined regulations, that would further energize the biogas industry.
Federal initiatives, such as the U.S. Renewable Fuel Standard, already influence this sector but hold room for further refinement. 13 Public polling reflects widespread support for increased federal investment in biogas capture from sources like dairy farms and landfills.
These policies create opportunities to boost liquefied natural gas production while addressing organic waste concerns. Growth projections point toward higher resource availability in the dairy farm and wastewater treatment sectors by 2025.
Opportunities in voluntary markets and collaboration with federal organizations
Voluntary markets now drive growth in renewable natural gas (RNG) and biogas investments. Companies commit to lower-carbon products, helping the industry expand without waiting for policy mandates.
For example, large corporations are sourcing RNG from dairy farms and wastewater treatment plants to meet sustainability goals. This demand pushes more facilities to capture biogas from organic waste from more sources like food wastes, crop residues (not just manure), and sewage treatment plants. 14
Federal organizations also play a key role in supporting this progress. Programs like the Rural Energy for America Program offer financial incentives for facility development in rural areas.
Bipartisan support further strengthens policies under initiatives like the Clean Air Act, encouraging innovation across sectors such as hydrogen production and energy recovery facilities.
This collaboration accelerates infrastructure expansion while maintaining peak power as clean and reliable as possible. 10
Innovation and Infrastructure Support
Biogas projects need a strong push in technology and tools. Boosting supply chains and building smarter systems can make this energy source more reliable.
Encouraging innovation and increasing the supply of biogas and RNG in the Dairy Farm and Wastewater Treatment Sectors
Expanding the supply of biogas from dairy farm manure requires bold strategies. The agricultural sector added 24% more digesters in recent years, bringing total operational units to 615. 1 These digesters process organic waste into valuable renewable natural gas (RNG), reducing methane emissions while creating clean energy fuels. Wastewater treatment facilities contribute as well, with nearly half of the existing biogas facilities located on-site.
Federal incentives and clear energy policies spark growth in these sectors. New investments target advanced technologies like cogeneration plants and biomass gasification systems to boost RNG production.
With over 15,000 potential new sites across the U.S., opportunities abound for transforming previously landfilled organic materials into sustainable sources of energy that power homes or vehicles. 1
Federal policies and financial support for the industry in the Dairy Farm and Wastewater Treatment Sectors
Federal policies like the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) define how the industry operates. This regulation supports biogas capture from dairy farm manure and wastewater treatment by promoting renewable energy.
Yet, uncertainty looms due to changing political landscapes, such as past shifts under the Trump Administration.
Tax credits also offer potential growth for energy recovery facilities within these sectors. The American Biogas Council actively pushes for revisions in financial policies to benefit waste-to-power projects.
Expanding collaboration with federal organizations could secure stable support for recycling organic material into clean sources of energy. 15
Conclusion to Biogas Capture in the Dairy Farm and Wastewater Treatment Sectors
Biogas capture is charging ahead in 2025. New facilities are springing up, and investments are flooding the market. With RNG capacity climbing and policies backing growth, the future looks bright.
Dairy farms and wastewater plants now lead energy recovery efforts with bold innovation. This industry isn't just growing; it's transforming how we power our lives.
FAQs
1. What is biogas capture, and how does it work?
Biogas capture involves collecting gases like methane from decomposing organic waste in landfills or wastewater treatment facilities. This gas can then be used for electricity generation or as a source of energy in fuel cells.
2. How will biogas capture grow by 2025?
New investments and advanced technologies predict record growth in biogas projects, especially for energy recovery facilities and thermochemical conversion processes.
3. Can biogas help replace traditional fuels?
Yes, biogas can serve as a renewable alternative to fossil fuels. It supports clean cooking initiatives and produces cellulosic biofuel while reducing harmful emissions like hydrogen sulfide.
4. What role does the Environmental Protection Agency play in biogas development?
The EPA promotes environmental protection through policies encouraging renewable identification numbers (RINs) and better management of leachate from landfills to protect soils and groundwater.
5. Why is recycling waste into power important?
Turning wastes into power reduces landfill use, cuts greenhouse gases, recycles resources like composted material, and boosts renewables that benefit both people and the planet.
References
- ^ https://www.constructiondive.com/news/rng-industry-data-report-2024-american-biogas-council/740363/ (2025-02-19)
- ^ https://www.wastedive.com/news/us-biogas-production-capacity-buildout-data-state-breakdown/750443/
- ^ https://biomassmagazine.com/articles/biogas-on-the-rise
- ^ https://www.biocycle.net/taking-pulse-of-the-biogas-industry/ (2025-02-25)
- ^ https://americanbiogascouncil.org/investment-in-new-u-s-biogas-systems-grows-by-3-billion-in-2024-a-40-increase-and-new-record/
- ^ https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/17/7/3144
- ^ https://www.wastedive.com/news/rng-industry-data-report-2024-american-biogas-council/740202/ (2025-02-18)
- ^ https://www.utilitydive.com/news/rng-industry-data-report-2024-american-biogas-council/740335/ (2025-02-18)
- ^ https://www.gp-radar.com/article/u-s-saw-record-investment-in-new-biogas-systems-in-2024
- ^ https://www.waste360.com/landfill/the-state-of-the-u-s-biogas-industry-and-policy-pushes-for-2025 (2025-02-17)
- ^ https://www.spglobal.com/commodity-insights/en/news-research/latest-news/energy-transition/060325-us-rng-infrastructure-expands-on-legislative-push-amid-market-headwinds
- ^ https://www.spglobal.com/commodity-insights/en/news-research/latest-news/energy-transition/021725-record-2024-brings-us-biogas-facility-count-to-nearly-2500-american-biogas-council (2025-02-17)
- ^ https://americanbiogascouncil.org/news-american-biogas-council/press-releases/
- ^ https://advancedbiofuelsusa.info/third-year-of-record-growth-for-u-s-biogas-industry-expected-to-continue-in-2024
- ^ https://americanbiogascouncil.org/new-poll-shows-broad-support-for-federal-investments-in-u-s-biogas-production/






