Food manufacturers are no strangers to food waste, with overproduction, strict quality control, and supply chain issues being just a few common challenges.
And while food waste is an unavoidable part of manufacturing, there are strategies you can implement to reduce your environmental impact—all while reducing costs and ensuring compliance.
As manufacturers face increasing regulatory pressure at state and municipal levels, the connection between food waste and anaerobic digestion presents a valuable solution. Interested in how it can help your facility stay compliant and control costs?
Keep reading to explore common challenges in the food manufacturing industry, how anaerobic digestion supports compliance, and more.
The Compliance Challenge Facing Food Manufacturers
In 2015, the U.S. Department of Agriculture and EPA announced the U.S. 2030 Food Loss and Waste Reduction goal, which aims to cut food loss and waste in half by the year 2030.
In response, an increasing number of food waste regulations have been introduced across the United States. And while this is a great initiative, these regulations can be difficult for companies that generate large volumes of waste like food manufacturers.
So what should you know about these new laws?
One of the most common regulations is organic landfill bans, which the Zero Food Waste Coalition defines as “a category of laws and regulatory requirements that restrict the amount of organic waste or food waste that can be disposed of in landfills or incinerators and/or require that food waste generators divert organic waste.”
In addition, manufacturers must also consider methane reduction targets, along with ESG and sustainability reporting requirements. Because many of these laws vary by state and municipality, staying up to date with local regulations is both critical and challenging for many companies.
If they don’t, they risk noncompliance—which can lead to fines, reputational damage, and added pressure across the supply chain.
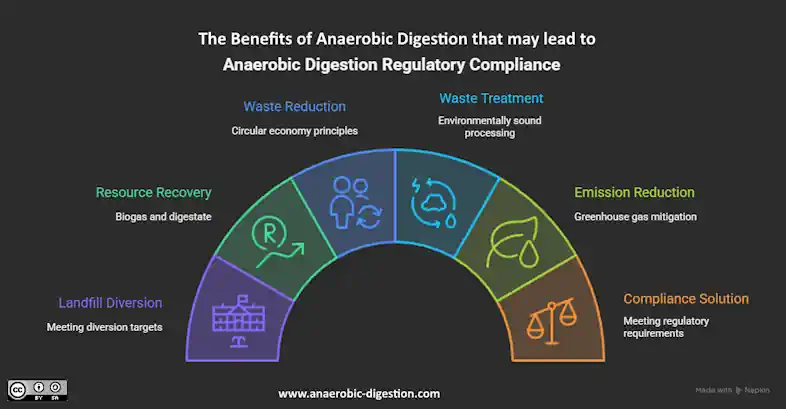
What Is Anaerobic Digestion?
Anaerobic digestion is a series of biological processes in which microorganisms break down biodegradable material in the absence of oxygen.
Simply put, manufacturers can send food waste and scraps to an anaerobic digester to divert waste from landfills and support sustainability goals. Beyond landfill diversion, anaerobic digestion also produces valuable outputs: biogas, a renewable energy source, and digestate, a nutrient-rich material that can be used as fertilizer.
Check out the image below to better understand the importance of these two outputs:
Source: EPA
Due to its ability to process large quantities of waste, create valuable outputs, and support a circular economy, anaerobic digestion serves as a valuable solution for food manufacturers.
How Anaerobic Digestion Supports Regulatory Compliance
Considering anaerobic digestion as a waste management solution?
Here’s how it can help you achieve regulatory compliance:
- Diverts organic waste from landfills
- Reduces methane emissions
- Supports local and state organics diversion mandates
- Aligns with ESG and sustainability initiatives

Cost Reduction Benefits for Food Manufacturers
Now that we’ve covered compliance, let’s discuss the ever-important topic of how anaerobic digestion can help cut costs.
- Reduced waste disposal costs: Landfill disposal costs are rising, so much so that the national average tipping fee has increased by almost 133% over 35 years. By diverting organic waste to anaerobic digestion, companies can reduce landfill tipping fees and gain more predictable waste management costs, making it a financially beneficial option.
- New revenue opportunities: Manufacturers that use the outputs of anaerobic digestion can also unlock new revenue streams. Potential opportunities include on-site biogas generation, electricity and heat offsets, and selling digestate as fertilizer for agricultural use.
- Operational efficiency gains: Anaerobic digestion can help companies streamline waste handling, reduce contamination issues, avoid noncompliance-related fees, and improve long-term cost forecasting. Together, these efficiency gains help manufacturers reduce operational risk while improving cost control over time.
On-Site vs. Off-Site Anaerobic Digestion Models
As you explore anaerobic digestion, you may wonder whether on-site or off-site systems are better for your company. Let’s compare these two options:
- On-site systems: On-site systems process food waste at the same location where the waste is generated. This option reduces transportation costs, gives companies greater control over the process, and can open up additional revenue opportunities, as discussed above. However, on-site systems require a high upfront investment, employee training, and ongoing management. While this option is often best suited for large manufacturers, it remains complex and out of reach for many companies.
- Off-site/third-party partnerships: Organizations that partner with third-party waste management providers benefit from lower capital risk and faster implementation. These partnerships also offer access to specialists who focus on compliance and cost-effective solutions, making this a common choice for many companies.
Before making a decision, every company should consider their waste volume, location, budget, and regulatory environment.
Real-World Use Case
To better understand the impact of anaerobic digestion, let’s take a look at a real-world case study highlighted by Mass.gov:
One of the nation’s largest producers of fresh onions reported peeling up to one million pounds of onions per day, generating roughly 300,000 pounds of onion skins and trimmings.
To streamline their waste management, the company turned to anaerobic digestion, using a system that presses juice from onion peels and feeds it into an anaerobic digester to produce methane-rich biogas. The remaining material is pressed into nutritious cattle feed.
The result?
A waste-to-energy system that saves $700,000 annually in electrical costs and $400,000 in hauling disposal costs—a win-win for the company and the environment.
Is Anaerobic Digestion Right for Your Facility?
If you’re debating whether anaerobic digestion is right for your company, it may be a good fit if:
- You generate large or consistent volumes of organic waste
- Rising disposal and hauling costs are driving up waste management expenses
- Your facility is subject to state or municipal organics diversion regulations
- You’re looking for more predictable waste management costs
- You want to reduce environmental impact while improving operational efficiency
If any of the above apply to your facility, anaerobic digestion could help support compliance efforts while reducing long-term costs. Many manufacturers start with phased adoption or pilot programs to evaluate feasibility before scaling.
Final Thoughts
Anaerobic digestion has emerged as a valuable solution for achieving sustainability goals, meeting compliance requirements, and reducing disposal costs.
As you explore your options, remember that reducing waste isn’t only a legal concern; it’s also an environmental responsibility. Reducing waste helps lower methane emissions, pollution, and resource depletion, making it a top priority for companies of all sizes.
So ask yourself: Could your company benefit from anaerobic digestion? What would implementation look like for your facility?






