Methane Facts – From AD to Greenhouse Warming of the Atmosphere: Methane is the main constituent in the gas produced by anaerobic digestion (AD) at usually about 60% of the total gas produced. Most of the rest is carbon dioxide.
It is also a fact that it's produced in large quantities from decaying organic wastes. And, one of man's biggest producers is municipal solid waste landfill along with all other types of organic material placed in landfills.
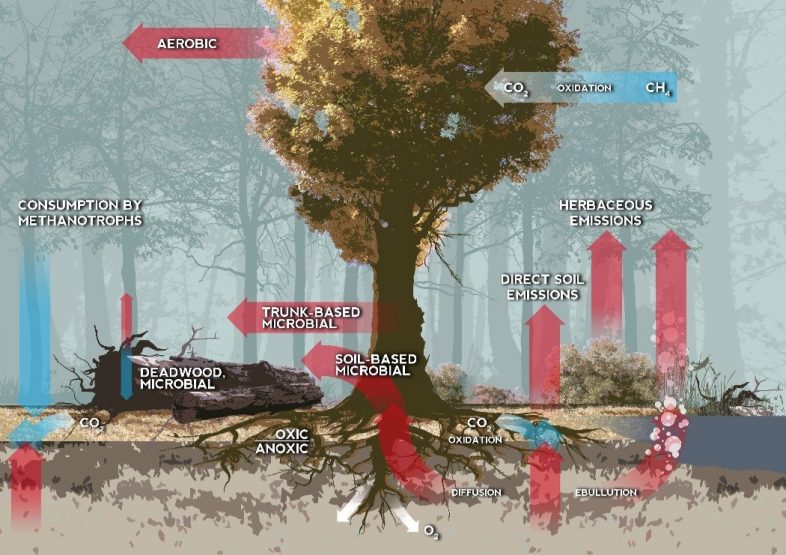
In the natural world peat, and thawing permafrost, produce methane. Coal beds also produce methane and it is major hazard to miners in coal mines, so our atmosphere already receives a large amount of methane every year, from natural sources.
Methane from Rubbish
Most avoidable man-made methane is generated as waste decomposes under anaerobic (without oxygen) conditions. The amount of methane created depends on the quantity and moisture content of the biological (organic) waste.
It is under most conditions lighter than air and very flammable. Methane is also “combustible”, meaning it will burn, and mixtures of about 5 to 15 percent in air are explosive.
Those are the methane facts! However, as methane is such a big global warming gas even accidental escapes increase global warming. These are called “fugitive methane emissions” and are explained in our video below. Watch Our YouTube Video about another aspect of Methane and its importance for Climate Change, below:
Other Facts About Methane
Methane is a clear odorless and tasteless gas which is lighter than air and not toxic when inhaled.
It can produce suffocation when it flows in such a manner that air is excluded. This can reduce the concentration of oxygen inhaled in a confined space to below the concentration needed for us to live.
In Different Situations it can be an Enemy or a Friend
Methane is a greenhouse gas that remains in the atmosphere for up to 15 years, but it is also a relatively inexpensive, clean burning fuel with a high heat content. If it is created from a renewable (regrowing) source, as part of earth's natural cycle of death, decay and regrowth does not cause climate change.
High Purity Methane
High purity methane is best known as “natural gas”, which currently is mostly produced from fossil fuels, and an extremely important energy source for many developed economies. Nonetheless, only part of the methane uptake in the atmosphere is due to industrial activities connected to energy production and use. Methane is the major constituent of natural gas. Purified biogas is called “biomethane”.
Why Methane is Much More Damaging than Carbon Dioxide as a Greenhouse Gas
Methane is a greenhouse gas 23 times more powerful than carbon dioxide.
Mostly considered to be because of human activities, our atmosphere's methane levels have more than doubled in the last 200 years.
It is produced naturally in wetlands and bogs, where it was once known as “willow-the-wisp”. It is of course a cause of death to miners when released while working in coal mines.
Coalbed methane, often referred to as CBM methane is stored within the coal by a process called adsorption. The methane is in a near-liquid state, lining the inside of pores within the coal (called the matrix). It can be released with little or no warning. While mining, workers need to be constantly monitoring for it and know how to escape when it is detected, before it builds-up to a dangerous concentration.
More Methane Facts
In the modern atmosphere, methane concentrations have risen by more than 150 percent since 1750. It's not clear whether this rise will continue, or at what rate, but the IPCC warns that keeping methane emissions in check is necessary in order to keep the planet from warming further. via nationalgeographic.com
Encyclopedic Methane Facts
Methane enters the atmosphere from both natural (30 percent) and anthropogenic (70 percent) sources. Methanogens (methane-producing bacteria in swamps and wetlands) are the largest natural source.
Anthropogenic sources of methane include leaks during fossil fuel mining, rice agriculture, raising livestock (cattle and sheep), and municipal landfills. Methanogens thrive in the oxygen-free (anaerobic) environment of landfills, releasing the gas in significant quantities. The gas is purposefully ignited to prevent explosion or captured for its commercial value as a fuel.
How Animals Create Methane
Livestock such as sheep, goats, camel, cattle, and buffalo currently account for 15 percent of the annual anthropogenic methane emissions. These grass-eating animals have a unique, four-chambered stomach. In the chamber called the rumen, bacteria break down food and generate methane as a by-product. Better grazing management and dietary supplementation have been identified as the most effective ways to reduce livestock methane emissions because they improve animal nutrition and reproductive efficiency. via www.encyclopedia.com
Methane is Lighter than Air – It's a well Known Fact!
Methane is lighter than air, having a specific gravity of 0.554. It is only slightly soluble in water. It burns readily in air, forming carbon dioxide and water vapour; the flame is pale, slightly luminous, and very hot. The boiling point of methane is −162 °C (−259.6 °F) and the melting point is −182.5 °C (−296.5 °F). via www.britannica.com
Molecular Scale Methane Information
Methane's molecular structure is very simple. It is a single carbon atom surrounded by four hydrogen atoms.
Methane can be produced by many chemical methods, but usually is found in natural gas and is obtained by fractional distillation, after it is become liquid.
Methane is used in industrial chemical processes and may be transported as a refrigerated liquid (liquefied natural gas, or LNG). via kids.kiddle.co