 You might ask why we are writing to explain “What are Bioplastics“, and relating them to the anaerobic digestion of waste. The reason is as follows; Bioplastics, or something like-named are being thrust into the news. That's a result of the recent realisation of the enormous scale of global plastics contamination which is now littering the oceans. The winning characteristic of bioplastics is that they can be readily biodegradable. They will not reside for generations in oceans, if they are left lying around. Right now, non-biodegradable plastics are causing huge numbers of wildlife deaths. When marine life which has lived in “plastic seas” is eaten by humans, small pieces of plastic inevitably also enter the human food chain.
You might ask why we are writing to explain “What are Bioplastics“, and relating them to the anaerobic digestion of waste. The reason is as follows; Bioplastics, or something like-named are being thrust into the news. That's a result of the recent realisation of the enormous scale of global plastics contamination which is now littering the oceans. The winning characteristic of bioplastics is that they can be readily biodegradable. They will not reside for generations in oceans, if they are left lying around. Right now, non-biodegradable plastics are causing huge numbers of wildlife deaths. When marine life which has lived in “plastic seas” is eaten by humans, small pieces of plastic inevitably also enter the human food chain.
What are Bioplastics: A Definition
Bioplastics are plastics derived from renewable biomass sources, such as vegetable fats and oils, corn starch, or microbiota.
Most bioplastics biodegrade more readily than commodity fossil-fuel derived plastics.
Bioplastic is generally used as the opposite of polymer derived from fossil resources.
Source: Wikipedia Bioplastic web page
But, this is misleading because it suggests that any polymer derived from biomass is environmentally friendly, which isn't always correct. IUPAC suggests that the alternative expression
“biobased polymer” be used, but it seems doubtful that many people will listen. “Biobased polymer” fails to roll-off the tongue anywhere near as easily as the term “bioplastics”.
Watch our video (below) on this subject, but do return when you have watched this video and scroll down beneath it, to where we have a lot more fascinating information about bioplastics, and what they are.
Bioplastics (Biobased Polymer) in the News!
There is a lot of interest in bioplastics right-now, many people are asking “What are Bioplastics”. That's because their use as a biodegradable form of plastic might help solve the current problem with the accumulation of non-biodegradable fossil fuel plastic, in oceans globally.
But there is a problem, because if bioplastics were to replace non-biodegradable petroleum-derived plastics, their higher cost and lower performance mean that they are likely to remain uncompetitive with old oil-based plastic.
Anaerobic Digestion of Waste Bioplastic
Depending on the rate of bioplastic fermentation in a biogas digester, biodegradable bioplastics can be digested to assist in producing methane.
If all plastic packaging used for food was biodegradable, it would hold big advantages for food waste anaerobic digestion plant operators.
Small pieces of non-biodegradable plastic materials which end up in the digestate, are currently a real problem for users of the digestate compost, especially for food waste AD plant operators.
Now, having read this, you should be able to answer the question; “What are Bioplastics”. We hope you found this article about “bioplastics and the Anaerobic Digestion of waste bioplastic” interesting.
Source: Wikipedia and European Bioplastics Organisation – Fact Sheet April 2015.Using Bioplastic Instead of Plastic for Packaging
In the contemporary scenario, much attention has been focused on extensive research across the globe to replace petroleum-based commodity plastics, in a cost-effective manner, with biodegradable materials offering competitive mechanical properties.
Bioplastics play an increasingly important role for consumer products. All these newly designed materials might increase product sustainability, but they are currently confined to niche markets. When compared to their petroleum-based counterparts, bioplastics can be biodegradable, sustainable, more environmentally friendly (lower greenhouse gas emissions and fossil fuel usage) and/or should be a renewable option to plastic product production.
Although there are still certain limitations in implementation of bioplastics as the main packaging materials, it remains a main material as a suitable replacement for petroleum-based plastics. Extensive research work is being done for comparing the superiority of bioplastic over conventional petroleum-based plastic under various conditions.
The main limitations lie in sourcing sustainable ingredients for building bioplastics and building materials with mechanical properties comparable to conventional plastics. via Alternative to plastic for packaging
Production of Biodegradable and Bioplastic Products
As above we said in “What are Bioplastics” above; bioplastics are those plastic materials that are manufactured by using natural resources. There are two categories of these plastics available in the market — biodegrable bioplastics and non-biodegradable bioplastics.
Demand for bioplastics is increasing since past decade due to growing awareness concerning environmental conservation, use of bio-based or natural resources for manufacturing materials and formulation of various regulations across countries for effective use of natural resources and waste management.
Products and solutions based on bioplastics/biopolymers present interesting opportunities globally. Opportunities are present across a variety of industrial sectors that include packaging, water, beverages, insulation materials, specialty materials and more.
The key factor driving the bioplastics market is the need for more eco-friendly and less polluting materials.
Other drivers include volatile fossil fuel prices and the need for companies to decrease their carbon footprint across their entire business value chain.
The demand for bioplastics has been gradually increasing due to its renewability and availability of raw material, advanced functionality and technical properties, and the recycling options at least some of them present. via Bio-Plastics Products Manufacturing
What are Bioplastics Growth Rates Going to be?
Bioplastic Packaging Market Size is Set to Value USD 34.24 Billion By 2024
 Fact-based market research, penetrating industry insights and validated forecasts to help you make better decisions for a stronger future
Fact-based market research, penetrating industry insights and validated forecasts to help you make better decisions for a stronger future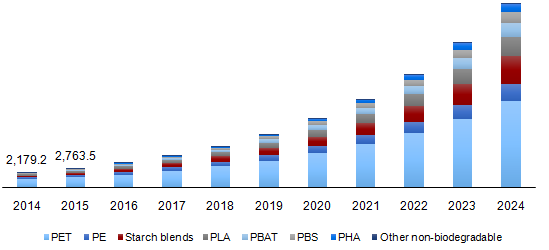
Felton, California, 2018-Feb-6 — /EPR Network/ — The global Bioplastic Packaging Market to reach USD 34.24 billion by 2024, driven by the rising consumer demand for resource efficient and eco-friendly products. Europe was the largest market accounting for 32.7% of the volume share in 2016 due to supporting regulations coupled with consumer awareness regarding the conservation of the environment. North America and Asia Pacific followed suit, where the regions together are expected to contribute USD 3.26 billion by 2024.
Keeping these driving factors in mind, companies are ramping up their production capacity as well as foraying into R&D of application of new biopolymers into mainstream applications. For instance, in October 2016, BASF and Avantium entered into a joint venture to form Synvina JV, which will manufacture and market FDCA and PEF. Synvina JV has a production capacity of 50,000 metric tons per year for FDCA and PEF.
Moreover, companies are focusing on R&D to expand the utilization of different raw materials such as PBS, PLA, and PBAT in various mainstream packaging applications. For instance, in April 2017, UK-based Biome Bioplastics developed a fully compostable and recyclable coffee cup made entirely from bioplastic materials. These factors together are expected to provide an impetus to the growth of the bioplastic packaging market over the next seven years. via Market Size USD 34.24 Billion
Video made by IPPTS – Contact us for a quote for your video at www.ippts.info




Is it okay to place a portion of this on my personal site? Reply by return if you don’t want this.
Thank you for your refreshing writing. It was a joy to reading Look forward to more articles from you!
Bye the way, did you know that, if you look up various pros and cons from the different distributors of green technology. Some let you know that although it can be pricey it is very beneficial for the environment to invest into green technology.
While others let you know that there are payment plans available when you invest in green technology. So make sure you do your research.
A very good read, on a very good blog, and I will be looking out for more of these articles. Do you think that something can actually be done about all this awful plastic pollution?
Don’t throw the baby out with the bathwater! Did you see Professor Thompson’s message — plastics are useful; they’re lightweight, durable and versatile. The challenge is how to keep the benefits of plastics without suffering the negative consequences. He’s Head of the International Marine Litter Research Unit, University of Plymouth.
Thanks for these very useful points. Keep the oceans healthy. Stop single use plastic. Very educational and as well as unique guidance on your topic.
Wow, that was a godd read. Somebody who really thinks. Quite hard to find these days, especially on the internet. But, seems tenuous to suggest biogas being made from bioplastics. I saved your blog and will make sure to keep coming back here, if this is how you usually post. thanks
This open access study came out about a year ago showing how PHB bioplastic biodegrades in Anaerobic Digestion.
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fenvs.2017.00093/full
AD research guy: Thanks for providing this link. It’s good to be able to read all of this open access study, and even better to read that in the conclusion that: “Bioplastic co-digestion at the loadings used increased biomethane production by 17%“.